Tool for developing software using the method of John C. Munson.
 7E550F - pseudocode control flow visualization
7E550F - pseudocode control flow visualization
In "Software Specification and Design" John C. Munson describes a process for developing software by successive refinement. The refinement is performed using a series of interconnected living documents describing the system.
Defining programs in this way allows for complete traceability from the user-level specification all the way down to code. It also allows for a variety of statistics about the quality of the resulting system to be computed. It can even be used to certify programs for use against various operation profiles generated from real-world usage or statistical models of usage.
Module Pseudocode Language
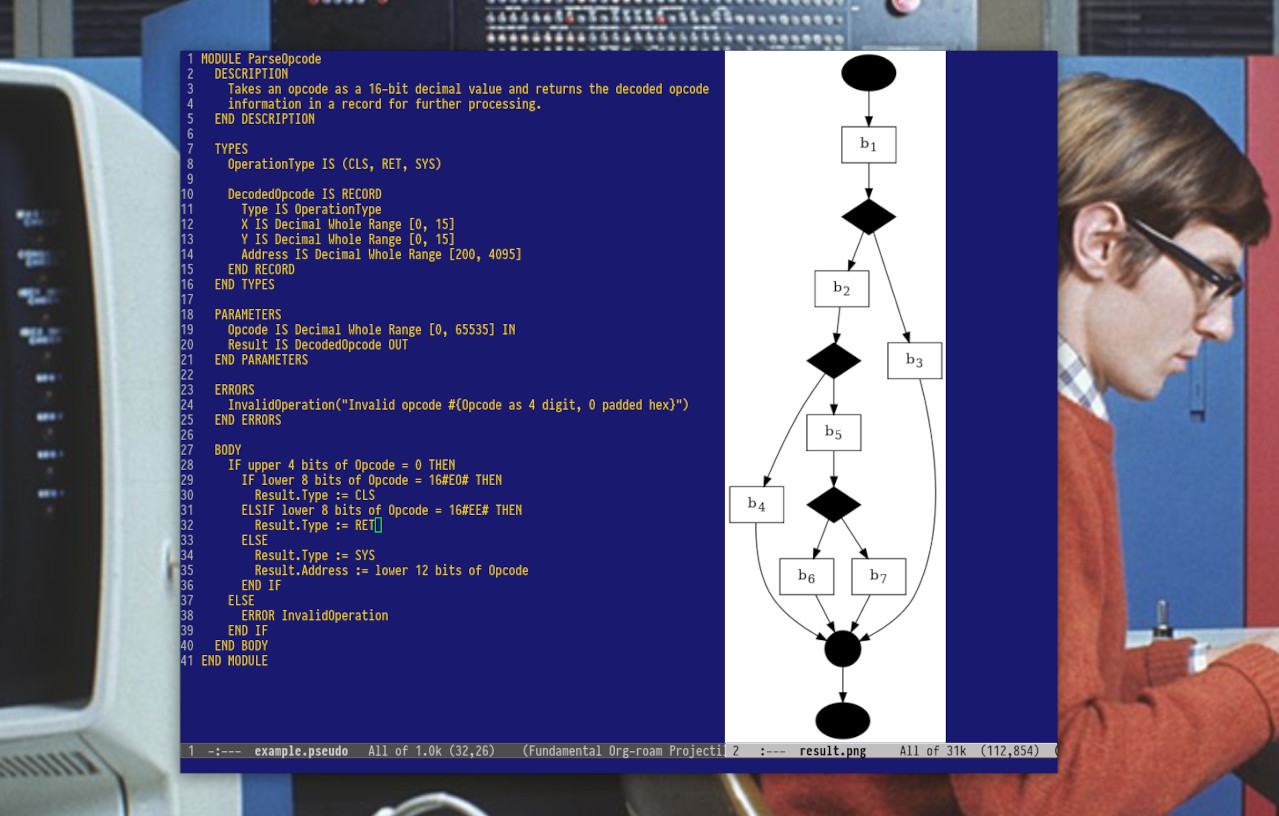
The munson tool provides a parser, analyzer, and visualizer for a module defintion pseudocode language. An example module for a Chip8 CPU emulator is shown below:
MODULE ParseOpcode
DESCRIPTION
Takes an opcode as a 16-bit decimal value and returns the decoded opcode
information in a record for further processing.
END DESCRIPTION
TYPES
OperationType IS (CLS, RET, SYS)
DecodedOpcode IS RECORD
Type IS OperationType
X IS Decimal Whole Range [0, 15]
Y IS Decimal Whole Range [0, 15]
Address IS Decimal Whole Range [200, 4095]
END RECORD
END TYPES
PARAMETERS
Opcode IS Decimal Whole Range [0, 65535] IN
Result IS DecodedOpcode OUT
END PARAMETERS
ERRORS
InvalidOperation("Invalid opcode #{Opcode as 4 digit, 0 padded hex}")
END ERRORS
BODY
IF upper 4 bits of Opcode = 0 THEN
IF lower 8 bits of Opcode = 16#EO# THEN
Result.Type := CLS
ELSIF lower 8 bits of Opcode = 16#EE# THEN
Result.Type := RET
ELSE
Result.Type := SYS
Result.Address := lower 12 bits of Opcode
END IF
ELSE
ERROR InvalidOperation
END IF
END BODY
END MODULE
Analysis of this module shows the following properties:
Module: ParseOpcode [Call Graph] In degree: 0 Out degree: 0 [Numerical Complexity] External: 29 bits Inbound: 16 bits Outbound: 12 bits Error: 1 bits Internal: 12 bits Data Type: 12 bits Variables: 0 bits Constants: 0 bits Total: 41 bits [Control Complexity] Paths: 4 Conditional Blocks: 6 Unconditional Blocks: 1 Method Calls: 0 Cohesion: 0.17
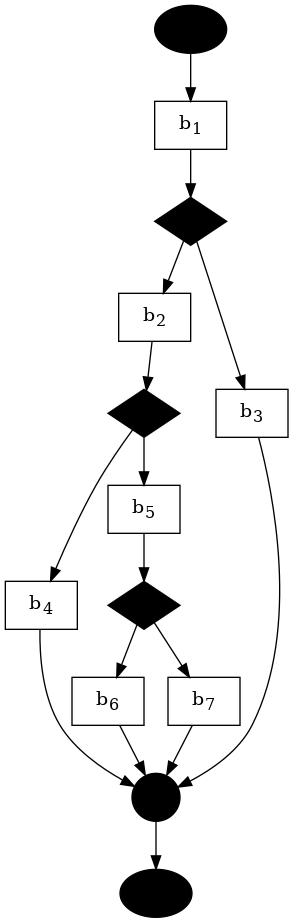
Running the visualizer displays the following control-flow diagram for the module:
incoming(1): software tools
Last update on 7E550F, edited 1 times. 2/2thh