Yawning abyss of the decimal labyrinth.
'in a crypto-kantian sense' - Kant's Critique of Pure Reason is basically a book about time. It argues that the relationship between thought and sensation is only possible because time 'already' provides an infrastructure supporting both sides). A 'schema' is required to connect an intellectual category with the 'pure intuition' (time and space) hosting appearances, thus enabling the emergence of an 'object' (a component of intelligible experience). This is why I thought the referencre especially relevant to Tachi's Q.s, which seemed in part to be asking whether the Numogram belonged to thought or to the world...A Kantian schema is situated in the 'between' ... and it's quite (hence 'crypto-') like a time-map.
- Nick Land, Numogram Q&A Comment
 - THE NUMOGRAM = 234 AQ = THE TIME GUIDE = NINE NINE NINE
- THE NUMOGRAM = 234 AQ = THE TIME GUIDE = NINE NINE NINE
The Hidden Numerals
The natural numbers, far from being boring asignifying entities rapdily appear more enigmatic, structured, and occulted the more one examines them. This fundamental structure is not just a curiosity but a toolset.
Every composite integer hides a subterranean link - via factorization - to the primes. The primes themselves are a field of singularities within number itself that always contains more structure than any known pattern can capture (see the Ulam Spiral).
Forming a composite number by multiplying primes is trivial compared to factoring a composite into its primes (a similar asymmetry-of-effort holds between differentiation and integration in Calculus). This one-way prime-composite asymmetry-of-effort allows very large primes to be operationalized for cryptographic ends.
Godel operationalizes the prime-composite relationship to encode formal statements as numbers used to conduct an assault on totalizing axiomatics. Land writes in "Mechanomics":
Godel-numbering accomplishes a revolutionary redirection of Kantianism - according to a nomad rather than a Copernican schema - by turning it towards the operationalization of transcendental synthesis as method, and away from the programmatic exhaustion of a self-limiting analytical endeavour. It converts the Kantian discovery of numerical synthesis from doctrinal commitment to procedural machinery: subsuming philosophy into transcendental arithmetic, with annihilating critique of the Hilbert programme as surplus product.
That is, Kant asserts that arithmetic rests on a rule-governed synthesis of time (schemata). In principle these rules are universal and a priori. However, Godel shows that any effective rule set attempting to capture arithmetic cannot be both complete and self-certifying. There is no single rule-complex that exhausts arithmetic truth. Thus, the synthetic a priori cannot be a closed system of truths codified by one set of rules but must be an open-ended transcendental process. Number becomes a medium not just for measuring but for thinking time itself.
Number Generates Hypertextuality
Gematria and other practices of linguistic numerical reduction generate hyptertextuality. They reveal subterranean connections between words and phrases generative of significance, meaning, or attention. Insofar as numerico-linguistic synchronicities add up they form a kind of blockchain or proof-of-work, cementing a set of relations as significant and non-trivial.
Numeracy disciplines literacy. The act of revising a name, phrase, title, or sentence until it generates a specific gematrical numerical value or word count encourages creative editorial iteration and a discipline of concision (or in terms of our principles, compression). And these are only a small handful of the ways - many yet to be discovered - that number can be productively put to work for human (?) ends.
The Numogram
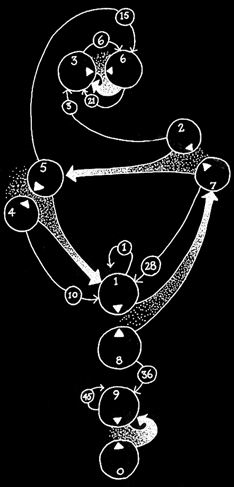
The Numogram is a diagram of the dynamics inherent in the decimal numerals. It is created from the decimal digits and the simplest of arithmetical operations. For any chosen operation there is only one requirement: the final (but not intermediate) result(s) must land firmly within the range 0-9. Thus, the operations chosen are: addition, subtraction, and digital roots.
Steps to recreate the numogram:
- Zones: Each digit 0-9 forms a zone.
- Syzygies: Group the zones into syzygys or pairs that sum to 9 (ex. 1 + 8 = 9, so 1:8 is a syzygy).
- Currents: Form currents from each syzygy to a zone by taking the positive difference between the zones in each syzygy (ex. 8 - 1 = 7, so create a current from 1:8 to 7).
- Gates: Form gates between zones by taking the digital root of the triangular number or digital cumulation of each zone number (ex. The 8th triangular number is 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 = 36. The digital root of 36 is 9. Therefore, form a link from 8 to 9.)
From this formulation and its rendering in the image above some initial properties appear:
- It is stratified from top-to-bottom into 3 strata.
- Warp: Upper stratum consisting of 3:6.
- Time Circuit: Middle stratum consisting of 1:8, 2:7, and 4:5.
- Plex: Lower stratum consisting of 0:9.
- The Warp and Plex appear to be inescapable "attractors" or "horizons" with one-way connections from the Time Circuit.
- The Warp forms a vortex or cycle. The Plex involutes purely within 9 (0 is the only number that digitally reduces to 0).
- The Time Circuit contains the same numbers that appear in the repeating (6-cycle) sequence produced by taking the digital roots of successive powers of 2: 1, 2, 4, 8, 7, 5, ...
Tic Xenotation
Tic Xenotation (TX) is a non-standard numeral notation that is both asignifying and that frustrates lexicographic ordering procedures on numbers. It is based on the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic (FTA) and represents each number >= 2 by its unique prime factorization. The definition:
- First prime: ':' or '0' = 2 (the 1st prime)
- Nth Primes: '(n)' = The nth prime (Ex. '(:)' = The 2nd prime = 3)
- Composite Formation (Multiplication): ':(:)' = 2 * 3 = 6
Note that TX cannot represent either 0 or 1 and there is some debate about this. A solution I like that also happens to not run afoul of non-visible characters:
- Zero: '*' = 0
- One (Zeroth prime): '(*)' = 1
There is also the possibility of Base-36 encoding TX to producing a string. For example:
(Decimal) 125 = ((:))((:))((:)) = 333 (Base-36)
Alphanumeric Qabbala
Alphanumeric Qabbala (also called Anglossic Qabbala) is simply another name for Base-36, a numerical base which includes all of the numbers 0-9 as well as the English Alphabet:
0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
English words and phrases can then be given a numerical value according to their Base-36 value. This numerical value is produced by summing the values of each letter.
Code
Below is some C source code for doing basic work with The Numogram, Alphanumeric Qabbala, and Tic Xenotation.
/*
================================================================================
oh4_numogrammatics.h - v1.0 - public domain
Authored 2025 by Eric Scrivner
no warranty implied; use at your own risk
Before including,
#define OH4NG_IMPLEMENTATION
in the file that you want to have the implementation.
ABOUT:
This header has been assembled (with gematric care) as a library of helpers
for the exploration of The Numogram or Numogrammatics.
USAGE:
The allocator (oh4ng_malloc) defaults to malloc but a custom method can also
be used to override that. For example, by doing:
oh4ng_malloc = MyCustomMalloc;
Allocation is only used by the following methods to build strings. These
methods can be made much more efficient (from 2 passes to 1 pass) by
reimplementing them with a linear or arena allocator:
void oh4ng_tx_from_number(int n, char** out_str, int* out_str_length)
void oh4ng_tx_base36_from_number(int n, char** out_str, int* out_str_length)
You can perform the basic operations of digital sum and root:
int oh4ng_digital_sum(int value)
int oh4ng_digital_root(int value)
You can get the nth triangular number as well as convert a triangular number
back to index:
int oh4ng_triangle_number_from_index(int n)
int oh4ng_index_from_triangle_number(int n)
There is also a set of methods for working with prime numbers as well as
getting nth prime number (or the index n from a given prime). You can also
retrieve the set of all prime factors for a given number:
int oh4ng_is_prime(int n)
int oh4ng_prime_from_index(int index)
int oh4ng_index_from_prime(int prime)
void oh4ng_prime_factors(int n, int out[32], int* out_count)
You can convert an integer into Base-36:
void oh4ng_base36_from_number(int n, char* buffer, int buffer_size, int* out_str_length)
You can also get the Anglossic or Alphanumeric Qabbala (AQ) reduction of a
string:
int oh4ng_aq_from_string(char* str, int length)
For Tic Xenotation (TX) you can encode and decode a number in TX using:
void oh4ng_tx_from_number(int n, char** out_str, int* out_str_length)
int oh4ng_number_from_tx(char* str, int length)
You can also encode and decode a number as Base-36 Tic Xenotation or TX
Base-36 using:
void oh4ng_tx_base36_from_number(int n, char** out_str, int* out_str_length)
int oh4ng_number_from_tx_base36(char* str, int length)
================================================================================
*/
#ifndef OH4_NUMOGRAMMATICS_H
#define OH4_NUMOGRAMMATICS_H
#ifndef OH4NG_DEF
#ifdef OH4NG_STATIC
#define OH4NG_DEF static
#else
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define OH4NG_DEF extern "C"
#else
#define OH4NG_DEF extern
#endif
#endif
#endif
/* Allocator definition (for building strings, defaults to malloc) */
OH4NG_DEF void* (*oh4ng_malloc)(size_t sz);
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_digital_sum(int value);
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_digital_root(int value);
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_triangle_number_from_index(int n);
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_index_from_triangle_number(int n);
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_is_prime(int n);
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_prime_from_index(int index);
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_index_from_prime(int prime);
OH4NG_DEF void oh4ng_prime_factors(int n, int out[32], int* out_count);
OH4NG_DEF void oh4ng_base36_from_number(int n, char* buffer, int buffer_size, int* out_str_length);
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_aq_from_string(char* str, int length);
OH4NG_DEF void oh4ng_tx_from_number(int n, char** out_str, int* out_str_length);
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_number_from_tx(char* str, int length);
OH4NG_DEF void oh4ng_tx_base36_from_number(int n, char** out_str, int* out_str_length);
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_number_from_tx_base36(char* str, int length);
#ifdef OH4NG_IMPLEMENTATION
static void* (*oh4ng_malloc)(size_t sz) = malloc;
static char* k_oh4ng_base36_ch = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_digital_sum(int value) {
int result = 0;
while ( value > 0 ) {
int digit = value % 10;
result += digit;
value /= 10;
}
return( result );
}
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_digital_root(int value) {
while ( value >= 10 ) {
value = oh4ng_digital_sum(value);
}
return( value );
}
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_triangle_number_from_index(int n) {
int result = ( n * ( n + 1 ) ) / 2;
return( result );
}
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_index_from_triangle_number(int n) {
int result = 0;
int low = 1;
int high = n;
while ( low <= high ) {
int mid = low + ( high - low ) / 2;
int triangle = oh4ng_triangle_number_from_index(mid);
if ( triangle < n ) {
low = mid + 1;
}
else if ( triangle > n ) {
high = mid - 1;
}
else {
result = mid;
break;
}
}
return( result );
}
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_is_prime(int n) {
int result = 0;
if ( n == 2 || n == 3 ) {
result = 1;
}
else if ( n < 2 || n % 2 == 0 || n % 3 == 0 ) {
result = 0;
}
else {
result = 1;
for ( int i = 5; i * i <= n; i += 6 ) {
if ( n % i == 0 || n % (i + 2) == 0 ) {
result = 0;
break;
}
}
}
return( result );
}
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_prime_from_index(int index) {
int result = 0;
if ( index == 1 ) {
result = 2;
}
else if ( index == 2 ) {
result = 3;
}
else if ( index > 2 ) {
int count = 2;
int candidate = 5;
while ( count < index ) {
if ( oh4ng_is_prime(candidate) ) {
count++;
result = candidate;
}
candidate += 2;
}
}
return( result );
}
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_index_from_prime(int prime) {
int result = 0;
if ( prime == 2 ) {
result = 1;
}
else if ( prime == 3 ) {
result = 2;
}
else if ( oh4ng_is_prime(prime) ) {
int count = 2;
int candidate = 5;
while ( candidate <= prime ) {
if ( oh4ng_is_prime(candidate) ) {
count++;
}
if ( candidate == prime ) {
result = count;
break;
}
candidate += 2;
}
}
return( result );
}
OH4NG_DEF void oh4ng_prime_factors(int n, int out_factors[32], int* out_factors_count) {
if ( n > 0 ) {
int factor_count = 0;
while ( n % 2 == 0 ) {
out_factors[factor_count++] = 2;
n /= 2;
}
for ( int i = 3; i * i <= n; i += 2 ) {
while ( n % i == 0 ) {
out_factors[factor_count++] = i;
n /= i;
}
}
if ( n > 1 ) {
out_factors[factor_count++] = n;
}
*out_factors_count = factor_count;
}
}
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_aq_from_string(char* str, int length) {
int result = 0;
for ( int idx = 0; idx < length; ++idx ) {
char ch = str[idx];
if ( ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) {
result += ( ch - '0' );
}
else if ( ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z' ) {
result += ( ch - 'A' ) + 10;
}
else if ( ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z' ) {
result += ( ch - 'a' ) + 10;
}
}
return( result );
}
OH4NG_DEF void oh4ng_base36_from_number(int n, char* buffer, int buffer_size, int* out_str_length) {
int length = 0;
/* Calculate required length */
if ( n == 0 ) {
length = 1;
}
else {
int v = n;
while ( v > 0 ) {
v /= 36;
++length;
}
}
/* Check if buffer has enough space (including null terminator) */
if ( buffer_size >= length + 1 ) {
buffer[length] = '\0';
if ( n == 0 ) {
buffer[0] = '0';
}
else {
int idx = 0;
int v = n;
while ( v > 0 ) {
int digit = v % 36;
buffer[idx++] = k_oh4ng_base36_ch[digit];
v /= 36;
}
}
}
*out_str_length = length;
}
OH4NG_DEF void oh4ng_tx_from_number(int n, char** out_str, int* out_str_length) {
#define oh4ng_tic_stack_max 64
char* str = 0;
int length = 0;
if ( n == 0 ) {
length = 1;
str = oh4ng_malloc(length + 1);
str[0] = '*';
str[1] = '\0';
}
else if ( n == 1 ) {
length = 3;
str = oh4ng_malloc(length + 1);
str[0] = '(';
str[1] = '*';
str[2] = ')';
str[3] = '\0';
}
else {
/* Two-pass algorithm: first count length, then build string */
int factors[32] = { 0 };
for ( int pass = 0; pass < 2; ++pass ) {
int counting = ( pass == 0 );
int write_idx = 0;
struct { int close_paren; int value; } tic_stack[oh4ng_tic_stack_max];
int tic_stack_idx = 0;
tic_stack[0].close_paren = 0;
tic_stack[0].value = n;
tic_stack_idx = 1;
while ( tic_stack_idx > 0 ) {
--tic_stack_idx;
int close_paren = tic_stack[tic_stack_idx].close_paren;
int v = tic_stack[tic_stack_idx].value;
if ( !close_paren ) {
int factors_count = 0;
oh4ng_prime_factors(v, factors, &factors_count);
if ( factors_count == 1 ) {
if ( factors[0] == 2 ) {
if ( counting ) {
length++;
}
else {
str[write_idx++] = ':';
}
}
else {
if ( counting ) {
length++;
}
else {
str[write_idx++] = '(';
}
/* Schedule close paren */
tic_stack[tic_stack_idx].close_paren = 1;
tic_stack[tic_stack_idx].value = 0;
++tic_stack_idx;
/* Schedule factor index */
tic_stack[tic_stack_idx].close_paren = 0;
tic_stack[tic_stack_idx].value = oh4ng_index_from_prime(factors[0]);
++tic_stack_idx;
}
}
else {
/* Composite: push all prime factors in reverse order */
for ( int idx = factors_count - 1; idx >= 0; --idx ) {
tic_stack[tic_stack_idx].close_paren = 0;
tic_stack[tic_stack_idx].value = factors[idx];
++tic_stack_idx;
}
}
}
else {
if ( counting ) {
length++;
}
else {
str[write_idx++] = ')';
}
}
}
if ( pass == 0 ) {
str = oh4ng_malloc(length + 1);
str[length] = '\0';
}
}
}
*out_str = str;
*out_str_length = length;
#undef oh4ng_tic_stack_max
}
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_number_from_tx(char* str, int length) {
int result = 0;
if ( length == 1 ) {
if ( str[0] == '*' ) {
result = 0;
}
else if ( str[0] == ':' ) {
result = 2;
}
}
else if ( length == 3 && str[0] == '(' && str[1] == '*' && str[2] == ')' ) {
result = 1;
}
else {
result = 1;
int idx = 0;
int valid = 1;
while ( idx < length && valid ) {
char ch = str[idx];
if ( ch == ':' ) {
result *= 2;
idx++;
}
else if ( ch == '(' ) {
int depth = 1;
int close_idx = idx + 1;
while ( close_idx < length && depth > 0 ) {
if ( str[close_idx] == '(' ) {
depth++;
}
else if ( str[close_idx] == ')' ) {
depth--;
}
close_idx++;
}
if ( depth != 0 ) {
/* Unbalanced parentheses */
valid = 0;
result = 0;
}
else {
int inner_length = close_idx - idx - 2;
if ( inner_length == 0 ) {
/* Empty parentheses */
valid = 0;
result = 0;
}
else {
int prime_idx = oh4ng_number_from_tx(str + idx + 1, inner_length);
int prime = oh4ng_prime_from_index(prime_idx);
result *= prime;
idx = close_idx;
}
}
}
else {
/* Invalid character */
valid = 0;
result = 0;
}
}
}
return( result );
}
OH4NG_DEF void oh4ng_tx_base36_from_number(int n, char** out_str, int* out_str_length) {
char* str = 0;
int total_length = 0;
int factors[32];
int factor_count = 0;
oh4ng_prime_factors(n, factors, &factor_count);
for ( int i = 0; i < factor_count; ++i ) {
int prime_idx = oh4ng_index_from_prime(factors[i]);
int segment_len = 0;
oh4ng_base36_from_number(prime_idx, 0, 0, &segment_len);
total_length += segment_len;
}
str = oh4ng_malloc(total_length + 1);
str[total_length] = '\0';
int write_pos = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < factor_count; ++i ) {
int prime_idx = oh4ng_index_from_prime(factors[i]);
int segment_len = 0;
oh4ng_base36_from_number(prime_idx, str + write_pos, total_length - write_pos + 1, &segment_len);
write_pos += segment_len;
}
*out_str = str;
*out_str_length = total_length;
}
OH4NG_DEF int oh4ng_number_from_tx_base36(char* str, int length) {
int result = 1;
for ( int i = 0; i < length; ++i ) {
char ch = str[i];
int prime_idx = 0;
if ( ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) {
prime_idx = ch - '0';
}
else if ( ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z' ) {
prime_idx = ( ch - 'A' ) + 10;
}
else if ( ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z' ) {
prime_idx = ( ch - 'a' ) + 10;
}
else {
/* Return partial result */
break;
}
int prime = oh4ng_prime_from_index(prime_idx);
result *= prime;
}
return( result );
}
#endif /* OH4NG_IMPLEMENTATION */
#endif /* OH4_NUMOGRAMMATICS_H */
Last update on 7E9B14, edited 1 times. 3/3thh
- 7E9B14 - The Numogram